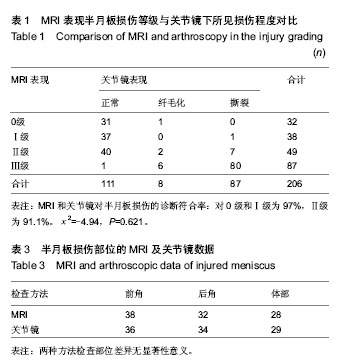
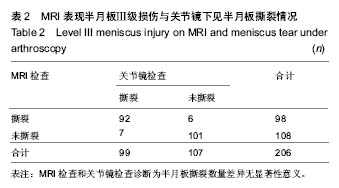
| [1] 敖英芳,胡跃林,余家阔,等.关节镜外科学[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2012:110.
[2] Wright RW,Boyer DS.Significance of the arthroscopic meniscal flounce sign:a prospective study.Am J Sports Med. 2007;2:242-244.
[3] Thomas S,rullagum M,Robinson E,et al.The value of magnetic resonance imaging in our current management of ACL and meniscal injures. Knee Stag Sports Traumatol Arthroec. 2007;5:533-536.
[4] Gregory CA,Prockop DJ,Spees JL.Non-hematopoietic bone marrow stem cells:molecular control of expansion and differetiation. Experimental Cell Res. 2005;(306):330-335.
[5] Stoller DW,Martin C,Crues JV,et al.Tears pathological correlation with MRI imaging.Radiology,2010;166: 4401-4402.
[6] 周根泉,张悦萍,马金忠.膝关节盘状半月板的MRI诊断[J].临床放射学杂志,2011,20(1):559-561.
[7] Fox MG.MR imaging of the meniscus: review,current t rends ,and clinical implications.Radiol Clin North Am. 2007; 45(6):1033-1053.
[8] Kean DM,Worthington BS,Preston BJ et al. NMR imaging of t he knee: example of normal anatomy and pathology.Br J Radiol. 1983;56:355.
[9] Michael G.MR imaging of themeniscus:review,current trends,and clinical implications.Radiol Clin North Am. 2007;45(6):1033-1053.
[10] Lyle NJ, Sampson MA, Barrett DS.MRI of intermittent meniscal dislocation in the knee.Br J Radiol. 2009;82(977): 374-379.
[11] Lowery DJ,Farley TD,Wing DW,et al.A clinical composite score accurately detects megiscal pathology. Arthroscopy. 2006;11:1174-1179.
[12] 涂茜,罗术祥,刘园园,等.MRI和X线检查在膝关节外伤诊断中的比较[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2005,3(1):54-56.
[13] 王淑丽,王林森,王植,等.膝关节盘状半月板类型及损伤的MRI分析[J].临床放射学杂志, 2004,23(1):66-69.
[14] Mageeth,Melboume F L,Willia MS D S.Utility of coronal MRimages of the knee.89th Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program,RSNA.Chicago:Mcromick Place, 2003: 48.
[15] He WL,Sam HK,Louis C,et al.Low-field MRI of the knee meniscus diagnosis of the clinical value.Department of Radiology. 2011;2:77-78.
[16] Kornick JK.Meniscal Abnormalities in the Asymptomatic Population at MR Imaging.Radiology.1990;8:411.
[17] Dillon EH,Pope CE,Jokle P, et al. Follow-up of Grad Meniscal Abnormalities in the Stable Knee. Radiology, 1991;181:894.
[18] 刘晓晟,许建荣,华佳,等.MRI对膝关节半月板撕裂诊断价值的Meta分析[J].中华放射学杂志,2007,41(7):731.
[19] Liu W,Lee LD,Yang C,et al.The test evalution of MRI in diagnosising meniscus injury of knee joint.J Practical Medical Techniques.2010;15:1485-1486.
[20] 刘泽坤,膝关节盘状半月板分型及损伤的MRI诊断表现分析[J].中外医疗,2012,(5):172-173.
[21] Friedrich KM,Mamisch TC,Plank C,et al.Diffusion-weighted imaging for the follow-up of patients after matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte transplanta- tion.Eur J Radiol. 2010; (73): 622-628.
[22] Sunny K,Jose B,John P,et al.Increase in outpatient knee arthroscopy in the United States:a comparison of national surveys of ambulatory surgery,1996 and 2006.J Bone Joint Sury Am.2011;93:994-1000.
[23] Bryan S,Weatherburn G,Bungay H,et al.The cost-effectivenessof magnetic resonance imaging for investigation of the knee joint.Health TechnolAssess.2001; 5(27):151-156.
[24] Khanda GE,Akhtar W,Ahsan H,et al.Assessment of menisci and ligamentous injuries of the knee on magnetic imaging: correlation with arthroscopy. Pak Med Assoc. 2008;58(10): 537-540.
[25] 赵泉,唐妮,伍小勇.膝关节损伤的MRI诊断及临床应用探讨[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学,2006,15(3):129.
[26] 尹东,孙可.膝半月板损伤的临床、MRI及关节镜对比研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(24):1873.
[27] 刘秀民,张振勇,王海波.低场MRI对膝关节内侧副韧带损伤的诊断及分级价值[J].中国医学创新,2012,9(6):73-74.
[28] Oei EH,Nikken JJ,Verstijnen AC,et al.MR imaging of the menisci and cruciate ligam- ents:a systematic review. Radiology.2003;226(3): 837-848.
[29] Helms CA.The meniscus recent advances in MR imaging of the knee.AJR.2002;179(6):1115-1122.
[30] De Smet AA,Mukherjee R.Clinical,MRI,and arthroscopic findings associated with failure to diagnose a lateral meniscal tear on knee MRI.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2008;190(1):22-26.
[31] Grossman JW,De Smet AA,Shinki K.Comparisonof theaccu-racy rates of 3-T and 1.5-T MRI of the knee in the diagnosis of meniscal tear.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193 (2): 509-514.
[32] Camacho MA.The double posterior cruciate ligament sign. Radiology.2004;233:503-504.
[33] Yoo JH, Hahn SH, Yi SR, et al.Posterior double PCL sign:a case resport of unusual MRI finding of bucket handle tear of medial meniscus.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007; 15(11):1343-5
[34] Brendan R,Barber,Eugene G,et al.Meniscal Injuries and Imaging the Postoperative Meniscus.Radi-ologic Clinics of North America.2013;51(3):371-391.
[35] 王成伟,李虹霖,赵博,等.MRI评价半月板损伤:基于SCI数据库10年的文献分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4):571-581.
[36] 陈辉,刘明军,王志强.前叉韧带及半月板损伤诊断方法比较[J].当代医学,2011,17(1):87-88.
[37] BenGalim P,Steinberg EL,Amir H,et al.Accuracy of m agnetic resonance imaging of the knee and un justified surgery.Clin Orthop.2006;447:100-104.
[38] Macarini L,Murrone M,Marinis S.MRI in the study of knee cartilage pathologies:influence of location and grade on the effectiveness of the method.Radio Med.2003;105:296-307.
[39] Yue BW,Gupta AK,Moorman CT,et al.Wrisberg variant of the discoid lateral meniscus with flipped meniscal fragments simulation bucket-handle tear:MRI and arthroscopic correlation. Skeletal Radiol.2011;40:1089-1094.
[40] 葛建忠,励钢.磁共振关节内增强扫描评价膝关节骨质、半月板、韧带和关节软骨损伤的准确性:与常规磁共振扫描比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(71):3078-3080.
[41] Stehling C,Souza RB,Helloi LE,et al.Loading of the knee during 3.0T MRI is associated with significantly increased medial meniscus extrusion in mild and moderate osteoarthristis. Eur J Radiol.2012;81:1839-1845. |
.jpg)